Conventional systems used in wastewater treatment have proven inadequate in achieving the desired effluent water quality, especially due to the wastewater pollution resulting from developments in the industry.
Additionally, considering the land costs required for treatment facilities, it is desired that treatment occurs in a smaller area and with high efficiency. Such requirements have led to the emergence and implementation of advanced treatment techniques that include new treatment technologies. Among the advanced treatment techniques today, the Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) process holds significant importance due to its wide application area.
The high cost of using membranes alone in wastewater treatment, the inability to achieve low discharge values with conventional systems, and the increasing importance of recovery in wastewater treatment have paved the way for the development of MBR. Following a two-year pilot-scale study, the world's first real-scale MBR facility was established in Porlock, England in 1994, aiming to meet the discharge standards of 500/100 ml total coliform and 100/100 ml fecal coliform in urban wastewater treatment.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBR) are advanced treatment processes used in wastewater treatment that combine biological treatment processes with semi-permeable membrane technology. If we consider that every technological advancement is a response to a problem, the most fundamental questions that come to mind for the birth of the MBR system are how to save space, how to increase treatment efficiency, and how to effectively recover wastewater. Compared to conventional biological treatment processes, the MBR system occupies much less space and has a high chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency for wastewater with lower biological degradability. Its small footprint makes it the preferred choice in areas where land costs are high.
Application Criteria of the MBR Process

The membrane modules used in membrane applications are classified as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. In MBR systems, the modules used are microfiltration and ultrafiltration with polymeric or ceramic membranes.
.png) .
.
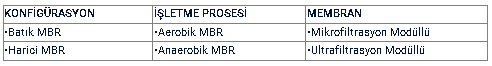
Wastewater is classified into ml;re. If we simplify this classification through a table;When wastewater enters an aerobic or anaerobic bioreactor, biological treatment begins, and simultaneous membrane separation occurs with biological degradation through a membrane cassette placed inside the bioreactor. The separation process is achieved by vacuuming the wastewater through vacuum pumps connected to the membrane cassettes, meaning it is filtered through the membrane. Systems where the membrane cassette is inside the bioreactor are called "Submerged MBR." If the membrane cassette is in a separate tank and the wastewater flows into this separate tank after biological treatment, it is referred to as "External MBR." There are some basic conditions that determine the choice between the two. In Submerged MBR, the flow rate is low, aeration costs are high, overall operating costs are low, initial investment costs are high, and the need for membrane cleaning is lower. In External MBR, the flow rate is high, but the need for membrane cleaning is greater, aeration costs are low, operating costs are higher, and initial investment costs are slightly lower. Looking at the general application, the submerged MBR system is used more frequently.The first figure below is an external MBR system. A membrane cassette has been placed in a second tank after biological treatment in the bioreactor. In the second figure, the membrane cassette is placed inside the bioreactor, using minimal space and achieving a more compact structure. Recently, in addition to submerged membrane applications, powdered activated carbon is also being added, allowing for the efficient removal of certain substances that cannot be removed through adsorption of pollutants in wastewater. Especially in wastewater containing pharmaceutical active ingredients that are difficult to biodegrade, powdered activated carbon can be added to the MBR tank.Figure 1: External MBR and submerged MBR, respectively.When looking at the type of operating process in MBR, the decision is made based on the selection of aerobic or anaerobic processes and the characterization of the wastewater. Industries with high pollutant loads, such as the food industry and confectionery industry, like...When selecting anaerobic MBR for industrial wastewater, aerobic MBR is preferred for wastewater from industries with lower pollutant loads and for domestic wastewater.The membrane module to be used in the MBR system depends on the particle size of the substances to be removed from the wastewater, and thus the suspended solids (SS) value. MBR systems are not only aimed at treating and discharging wastewater but also target the recovery of wastewater. Depending on the application where wastewater will be recovered (such as garden irrigation, machine cooling water, boiler-machine washing water, etc.), the type of membrane is determined, and microfiltration or ultrafiltration membranes are selected.The main problem encountered in MBR systems is the clogging of membranes due to fouling, which prevents obtaining the desired flow rate. If the clogging is standard, it can be resolved through physical methods and chemical cleaning. The physical method is performed by backwashing with permeate water or air. In physical cleaning, while the system is operating, adjustments are made automatically, for example, backwashing for 2 minutes every 30 minutes of filtration. In cases of fouling that cannot be resolved by physical cleaning due to prolonged operation of the system, the membrane and module are separated, and a chemical cleaning process is applied using hypochlorite or sulfuric acid. Fouling that cannot be removed by chemical cleaning is referred to as irreversible fouling, and the system can only continue to operate with the replacement of membranes. Depending on the characterization of the wastewater and operating conditions, membrane lifetimes vary between 6-10 years.In many sources, one of the disadvantages of MBR applications is that the initial investment cost is high due to the cost of membrane use compared to a conventional activated sludge application. Here, the cost of the membranes used in the MBR facility, which increases the initial investment cost, should be compared with the savings in land costs due to the smaller area required for the establishment of the facility. After this comparison, although the membrane represents a significant cost, especially in areas like Istanbul where land costs are high,In regions where high costs are incurred, the initial investment cost may shift in favor of MBR and can turn from a disadvantage into an advantage.**Global Market for MBR Applications**The MBR system reached a level of 1.5 billion dollars worldwide in 2015 among treatment technologies. In the treatment of domestic wastewater with MBR, companies such as Kubota, Mitsubishi Rayon, Zenon, Tianjin Motimo, Toray, and Origin Water Technology dominate 80-85% of the market. Membrane suppliers from the USA and Germany (such as GE-ZeeWeed, Siemens Water Tech, etc.) are also established companies in the market.When examining the 20 largest projects in the world that used MBR technology for wastewater treatment until 2010, it is seen that there is a wastewater treatment capacity of 1,157,000 m3/day, with the largest project being the Shending River MBR facility in China, which treats 110,000 m3/day of wastewater. Between 2010 and 2017, the treatment capacity of 20 projects established with the MBR system in China was found to be 3,003,000 m3/day. Five of these projects have a treatment capacity of over 200,000 m3/day. In just seven years, the development in the MBR sector in China has tripled the global data from seven years ago. As can be understood from this comparison, MBR applications are growing very rapidly in the sector.**Current Situation of MBR Applications in Turkey**In Turkey, rather than large-capacity treatments, package treatment models providing 50-100 m3/day of treatment are more commonly encountered. In our country, the focus of wastewater treatment is not just on discharging into the channel but on recovering and re-evaluating wastewater to prevent the depletion of water resources.The understanding that it is a process has not developed to the desired level. The first large-scale membrane bioreactor system that can be considered significant in Turkey was established at the ODTÜ (Middle East Technical University) campus for research purposes to use the effluent for irrigating the campus lawns. The facility, with a treatment capacity of 200 m3/day, has saved approximately 240 thousand TL annually in lawn irrigation costs. The number of relatively large-scale urban wastewater treatment plants using MBR is four. A brief overview of these facilities is as follows:Konacık (Muğla) MBR Wastewater Treatment Plant; has a wastewater treatment capacity of 3,000 m3/day and is built on an area of 3,600 m2. The treated water is used for park and garden irrigation. The project and construction cost is approximately 9 million TL (2011).İznik (Bursa) MBR Wastewater Treatment Plant; has a wastewater treatment capacity of 9,000 m3/day and is built on an area of 7,045 m2. The treated waters are discharged into Lake İznik. The project and construction cost is approximately 13 million TL (2013).Finike (Antalya) MBR Wastewater Treatment Plant; has a wastewater treatment capacity of 17,000 m3/day and is built on an area of 7,725 m2. The treated waters are discharged into a stream. The project and construction cost is approximately 15 million TL (2011).Gazipaşa (Antalya) MBR Wastewater Treatment Plant; has a wastewater treatment capacity of 13,650 m3/day and is built on an area of 24,000 m2 (half of the area is vacant). The treated waters are discharged into a stream. The project and construction cost is approximately 11 million TL (2011).When the area occupied by treatment plants is compared to the population they serve in Turkey; the average treatment area per person for long aeration activated sludge treatment plants is found to be 0.57 m2, while for membrane bioreactor technology wastewater treatment plants, it is 0.15 m2.**Did You Know About the Development of the Main Component of MBR Membranes?**In the first membrane applications, animal skin and intestines were used. The first documented membrane-diffusion experiment was conducted in 1748 when French Abbe Nollet stretched an animal skin over the mouth of a barrel filled with wine and submerged the barrel in water. Although water entered the barrel, the wine could not pass through the skin and escape. Thus, osmosis...It was discovered. During World War II, the drinking water networks of the Germans were damaged during air bombardments, leading to the development of microfiltration membranes at Hamburg University. Thus, the first large-scale water purification process was carried out to obtain drinking water using membranes. In 1946, membranes were first used in the medical field for artificial kidney devices in hemodialysis.
.jpeg)



