In prehistoric times, humans met their basic need for nutrition through hunting and gathering, while their need for shelter was fulfilled by caves, tree hollows, or rock shelters found in nature. These activities triggered a nomadic lifestyle.
However, over time, improvements in climate conditions have allowed people to stay in a region for a relatively longer period. When this is combined with the accumulation of knowledge among people, developments began to emerge, enabling humans to dominate nature.
In this article, we will discuss the history of copper from the past to the present, its areas of use, the situation of copper in wastewater generated during production activities, and methods of treatment and recovery.
The History of Copper and Copper Reserves in Turkey
The discovery of copper, one of the metals from the prehistoric period, dates back to around 5000 BC. It is believed to be one of the oldest metals used by humanity. The reason for this is that copper can be found in knives and tools known to belong to the Stone Age, as well as in more advanced tools and objects from the Bronze Age.
The emergence of copper was a coincidence. Some scenarios close to reality can be generated regarding the discovery of copper. For example, an Egyptian living in prehistoric times might have dropped a piece of malachite into a glowing fire and seen copper flow in shiny droplets; or the fire lit by someone searching for precious stones on a copper ore close to the surface might have reduced the ore and transformed it into copper. With the discovery of the metal towards the end of the Stone Age, copper greatly contributed to the development and advancement of civilizations around the world. As the first metal discovered by humankind, copper could be used in many areas at a very low cost. Studies related to copper reserves in our country are conducted by the General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration, Black Sea Copper Enterprises, Etibank, and the private sector.
Turkey has two important regions in terms of copper reserves: the Eastern Black Sea and Southeastern Anatolia Regions. All copper reserves found in Turkey are shown on the map above.
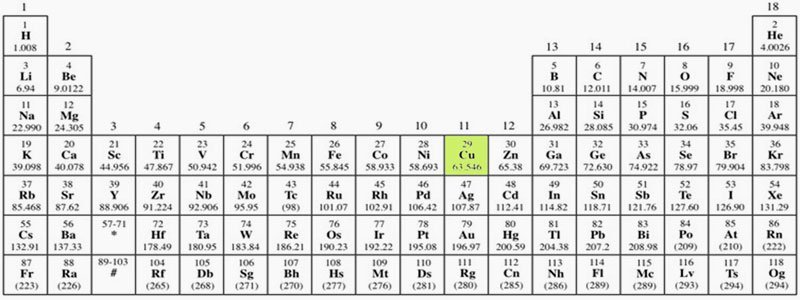
The Place and Properties of Copper in the Periodic Table
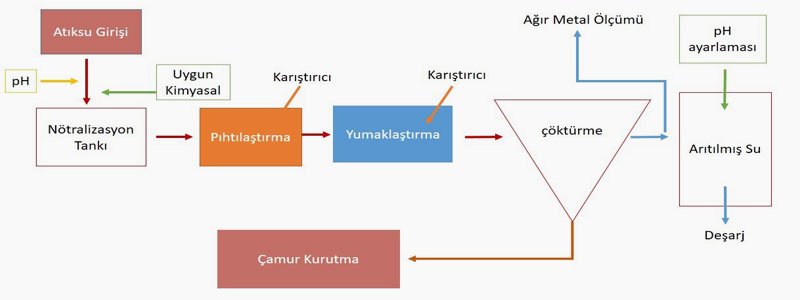
When you learn where the name of the copper element comes from, you might be a little surprised. The copper element was found in quite large quantities in Cyprus. Indeed, the name of copper in foreign languages also comes from Cyprus. The Romans extracted copper from Cyprus and called it "Aæs Cyprium." This name was later shortened to the Latin name "Cuprum." It then transformed into "Kyprios" in Greek, "Copper" in English, and "Kupfer" in German. Its symbol also comes from the first two letters of its Latin name. Another view is that the name Cyprus is derived from copper.Copper is a solid chemical element in group 1B with atomic number 29. Due to its widespread availability in almost all regions of the Earth, its excellent conductivity of electricity (second only to silver among all metals), and its high industrial importance in making alloys like brass and bronze, copper has a wide range of applications.**Uses of Copper**Copper, one of the natural materials offered to humans by nature, can be found in free or combined forms. Due to its high conductivity, copper is generally used in areas where heat and electricity need to be transmitted. With its reddish color, copper is one of the most widely used ores and has been used since ancient times due to its ease of production. The areas where it is most commonly used are listed below.**What Are the Effects of Copper on the Environment and Human Health?**As mentioned above, copper, which is widely used in many areas, is classified as a heavy metal. Heavy metals are found in wastewater generated from industrial activities, leachate from landfills, and water that seeps from mining sites due to rain, etc. These waters mix with receiving environments such as lakes, rivers, and groundwater, and accumulate in sediments. Therefore, from the discharge point, the weight...They protect pollution values without losing them even from meters away. Metallic pollution cannot be broken down by chemical and biological methods. Thus, heavy metals that reach the food chain cannot be eliminated chemically and biologically and accumulate in the body.Heavy metals that may be found in wastewater cannot be biologically degraded like organic compounds. The widespread use of certain heavy metals leads to their presence in unwanted concentrations in wastewater. These heavy metals, which are found in high amounts in the wastewater of various industries, are listed as "priority pollutants." Especially, the coating, mining, and metal alloy industries have high concentrations of heavy metals in their waste and wastewater.The discharge of copper-laden wastewater resulting from industrial activities into the environment without treatment or reduction to desired values has harmful effects on the environment and consequently on humans. Excessive copper in water is particularly toxic to bacteria, seaweeds, fungi, and fish. Excess copper ingested by humans causes disorders in the liver and stomach.Due to these environmental effects, the concentration of copper in wastewater must be reduced to a certain limit value. When discharging into the receiving environment, it is done by ensuring that the limit values in the relevant sector table of the Water Pollution Control Regulation (WPCR) are met. Outside the receiving environment, when discharging to units with wastewater infrastructure such as Organized Industrial Zones, Free Zones, and Municipalities, compliance with the limit values determined by the channel owner management based on the sectoral table parameters specified in the WPCR is required.**What Methods Are Selected for Copper Removal in Wastewater? Can Copper Be Recovered?**Copper in wastewater is removed through processes such as chemical precipitation, coagulation-flocculation, ion exchange, and electrochemical methods. The disadvantages of these methods include incomplete removal of heavy metals, high energy costs, and the production of toxic sludge. In recent years, wastewater containing heavy metals...Adsorbents, membrane separation, and electrodialysis methods have started to be used in the treatment of wastewater. However, the optimal treatment method must be the one that causes the least harm to the environment and is sustainable. These treatment methods generally depend on the characteristics, quantity, and environmental conditions of the wastewater. In this article, we will discuss commonly used methods.**An Inexpensive and Easy Method: Chemical Precipitation!**The most widely used method for the removal of heavy metals in wastewater both globally and in our country. In this process, the aim is to remove heavy metals from the environment by precipitating them to the bottom with an appropriate chemical. The pH of the environment is quite important for the process.Heavy metals are generally removed from the environment by precipitation with lime and limestone at a high pH (9-11). Since they exist in a soluble form at low pH, the pH of the environment is first raised to perform chemical precipitation. A simple schematic representation of the chemical precipitation process is shown on the left.The removal of heavy metals by chemical precipitation is the most economical method. Its applicability is simple. The disadvantage of chemical precipitation is the chemical sludge that forms as a result of the precipitation. Since this sludge falls into the category of hazardous waste, it must be disposed of through special processes.**Copper Removal by Coagulation-Flocculation Method**Another method that is quite frequently used in heavy metal removal. First, suspended solids (SS) that are stably present in the wastewater are made unstable, and then flocculation is performed by increasing the particle size. The formed flocs are removed from the environment by sedimentation. The optimum pH range for heavy metal removal through chemical coagulation-flocculation with sulfur is between 11 and 11.5. Therefore, the pH of the wastewater is primarily adjusted to the appropriate range using strong bases such as sodium hydroxide. Then, a coagulant is added to the environment.is achieved. In this method, water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane, allowing only certain molecules to pass while rejecting others. This results in a significant reduction of copper concentration, achieving up to 99% removal efficiency for heavy metals. The advantage of this method is its high efficiency in a compact area. However, issues such as membrane fouling, reduced membrane resistance, and slow liquid flow due to material degradation can lead to increased operational costs.Nanofiltration (NF) has a lower energy consumption due to its looser membrane structure and is quite effective for copper removal. However, it has not yet become widespread due to insufficient research on membrane stability and process condition optimization.Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a purification method that allows liquids to pass through semi-permeable membranes. This method accounts for 20% of the desalination of saline waters worldwide.nd adsorpsiyon kapasitesi ile etkili bir adsorbenttir. Adsorpsiyon yöntemi, metal iyonlarının yüzeyde tutulması ile gerçekleşir ve bu süreçte metal iyonları, adsorbent yüzeyine bağlanarak çözeltiden ayrılır. Bu yöntem, özellikle düşük konsantrasyonlu atıksularda ağır metal giderimi için etkili bir yöntem olarak kabul edilmektedir.Due to its adsorption capacity and surface reactivities, it can be used. Technical feasibility and price are the most important factors in the selection of adsorbents.### Recovering Copper from Wastewater: Ion ExchangersIn the ion exchange method, dissolved copper in wastewater is separated from the medium by exchanging places with cations (such as hydrogen, sodium, potassium) in the ion exchange resin. These types of reactions are reversible. After ion exchangers reach a certain saturation, they can be regenerated and reused. The solutions used for the regeneration process vary according to the selected ion exchangers.In the ion exchange process, selecting the appropriate ion exchanger, the pH of the medium, contact time, and temperature are important. If the contact time is insufficient, the process may not be efficient. It is known that ion exchangers operate at maximum efficiency when the ambient temperature is between 0-35 °C.In the removal of copper with ion exchangers, the absence of treatment sludge is a significant advantage. As a result of this process, valuable heavy metals can be recovered in a concentrated medium with appropriate solutions. However, if there are other heavy metals in addition to copper in the medium, multiple ion exchangers will be used, which may increase operating costs accordingly.## Recovery or Treatment?Copper can be recovered from wastewater or from sludge removed by precipitation. There are multiple parameters that affect the recovery of copper. These include the pH of the medium, copper concentration, the method used, and operating costs. In fact, the commercial value of the recovered copper determines the attractiveness of the recovery method. For wastewater containing copper below 200 mg/L, ion exchange and activated carbon methods are more economical. Copper can be effectively removed with activated carbon. At alkaline pH, copper precipitates as a low solubility metal hydroxide. If there is a high amount of sulfate in the medium, the recovery of copper from the resulting sludge may not be economical.It has been determined that the lowest copper level that can be economically achieved through chemical precipitation is 0.02-0.07 mg/L. At a pH of 8.5, copper levels in the effluent can be reduced to 0.01-0.02 mg/L as a result of precipitation (flocculation-coagulation) with sulfur. The presence of complex-forming ions such as cyanide and ammonia in wastewater makes it difficult to achieve low copper levels in the treated water. For high copper removal, these ions need to be removed through pre-treatment.In conclusion, if conditions are suitable, the recovery of copper and precious metals is necessary. This way, both the environment and human health are protected, and it contributes to the circular economy as an input. In this context, as Artemis Treatment, we continue our studies aimed at improving our current applications by prioritizing our R&D activities. Sourceswww.mta.gov.tr/mta_web/kutuphane/mtader gi/13_4.pdf
Oğuz B., “The Source of Non-Ferrous Metals”, OERLIKON Publication (1990)
TUĞRUL, D., “Determination of Some Elements in Pinus Radiata by AAS”, Master's Thesis, Kocaeli University Department of Chemical Engineering, Kocaeli, 1999.
SEZGİN, N., “Investigation of Heavy Metal Removal from Industrial Treatment Sludges”, Doctoral Thesis, Istanbul University Department of Environmental Engineering, Istanbul, 2012
ESENBOĞA A., “Recovery of Copper, Nickel, and Zinc from Waste Solutions by Solvent Extraction Method”, Master's Thesis, Istanbul Technical University Institute of Science, Istanbul, 2014
HARMAN H., “Treatment of Copper-Containing Wastewaters from Plants Producing Copper Chemicals by Ion Exchange Method”, Master's Thesis, Istanbul Technical University Institute of Science, Istanbul, 2010