The development of modern industry has continued for several hundred years, and up to the present day, three major industrial revolutions have emerged. Currently, we have entered the fourth industrial revolution, known as Industry 4.0.
Industry 4.0 aims to take over production with robots that can communicate with each other, perceive the environment with sensors, and recognize needs through data analysis; it seeks to create a production process that is of higher quality, cheaper, faster, and produces less waste. Additionally, Industry 4.0 allows for communication between objects and humans by monitoring physical processes with cyber-physical systems in modular smart factories, resulting in decentralized collaborative decision-making. In today's competitive environment, it has become inevitable for businesses to implement Industry 4.0 in their organizations to maintain and sustain their existence through simple digital marketing tips.
Four Major Industrial Revolutions Have Occurred Throughout History
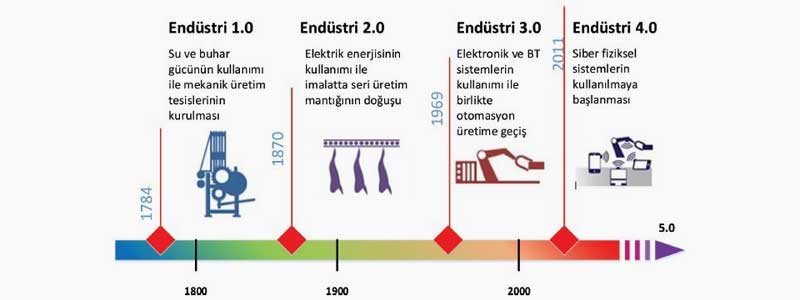
These are;
- The discovery of mechanical tools that enable more efficient use of water and steam power,
- Henry Ford's design of the assembly line and the beginning of electricity's use in mass production, leading to the development of the production line,
- The use of programmable machines in the 1970s, which caused mechanical and electronic technologies in production to give way to digital technology. Today is within this industrial revolution.
- Industry 4.0 is considered an industrial strategy plan that is thought to initiate the 4th Industrial Revolution.
The Structure of Industry 4.0

Industry 4.0 is a collective whole of technologies and concepts of value chain organizations. It is based on the concept of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, and the Internet of Services. This structure greatly contributes to the formation of the vision of smart factories. Industry 4.0 generally consists of the following 3 structures.
- Internet of Things
- Internet of Services
- Cyber-Physical Systems
With Industry 4.0, within the scope of modular smart factories, monitoring physical processes with cyber-physical systems, creating a virtual copy of the physical world, and central
the goal is to make decisions that do not exist. The Internet of Things and cyber-physical systems will be able to communicate with each other and with humans in real-time and work in collaboration. With the Internet of Services, both internal and cross-organizational services will be offered and evaluated by the users of the value chain.Industry 4.0 fundamentally aims to bring together Information Technologies and Industry. The first of its main components is new generation software and hardware, which, unlike today’s classical hardware, are low-cost, space-saving, energy-efficient, produce little heat, yet operate with high reliability, and the operating and software systems that run this hardware are aimed to be economical in terms of resource and memory usage. The second and perhaps most important component is the Device-Based Internet (IoT), where all devices on Earth are used for exchanging information and data, integrated with all kinds of tools and equipped with sensors and actuators, and we can briefly call this system Cyber-Physical Systems.The use of cyber-physical systems in machines in factories during the production process means that 'smart factories' can produce by coordinating and optimizing themselves almost independently of humans. If the Industry 4.0 strategy is realized, the production time, costs, and the amount of energy required for production will decrease, while the quantity and quality of production will increase.**Principles of Industry 4.0**Industry 4.0 is based on 6 principles.1. Interoperability: The ability of cyber-physical systems (e.g., workpiece carriers, assembly stations, and products) to communicate with each other through the Internet of Things and the Internet of Services, involving people and smart factories.
2. Virtualization: This structure is a virtual copy of smart factories. The system is formed by connecting sensor data with virtual facilities and simulation models.
3. Autonomous Management: Cyber-Physical...The ability of autonomous systems to make their own decisions within smart factories.
Real-Time Capability: The ability to collect and analyze data. This structure allows for rapid understanding.
Service Orientation: Cyber-physical systems, people, and smart factory services are provided over the Internet of Services.
Modularity: Provides a flexible adaptation system for smart factories to changing requirements. **Advantages of Industry 4.0** 1. Facilitation of system monitoring and fault diagnosis
2. Self-awareness of systems and components
3. Sustainability of the system with eco-friendly and resource-saving behaviors
4. Achievement of higher efficiency
5. Increased flexibility in production
6. Reduction of costs
7. Development of new services and business models **Application Areas** **Smart City Applications** Implemented in areas such as traffic, parking, lighting, and municipal waste management. The data transmitted to you regarding the predicted traffic density in the maps section of your smartphone when you hit the road in the morning is entirely the result of applications made in this field. **IoT Applications for Building and Home Automation** From increasing security to reducing energy and maintenance costs, monitoring and controlling smart buildings and smart homes. IoT products and systems aimed at smart buildings and homes currently used in the sector include connecting home devices to the internet, network gateways, light control, smart locks (electronic-controlled locks instead of mechanical locks), smart thermostats, Wi-Fi weather sensors, Wi-Fi controlled lighting systems, video doorbells (seeing who has come home remotely with a smartphone), building/home entry control panels, etc. **Smart Manufacturing**0 projects will be elevated to a higher level with software and hardware. We can count IoT products and systems aimed at smart factories currently used in the industry as CPU (PLC control), hydraulic valves, pneumatic valves, portable monitors, process analysis, robotic control, CPU cards, long-range field transmitters, etc.**Wearable Products**From wristbands that track how many calories you burn by monitoring your daily activity to bands that measure your ECG, many different products are quickly accessible today. Currently used wearable IoT products can be counted as augmented reality and entertainment, smartwatches, and location and tracking, etc.**Smart Environment Applications**It is applied to collect predictive data related to many natural events such as air pollution, rain and precipitation status, dam fill rates, forest fires, snow, blizzards, and storms. Smart home applications enable remote management of services provided or to be provided by homes in areas such as lighting, security, illumination, and entertainment, both inside and outside the home. For example, you can turn your lights on or off by connecting to smart home applications remotely. The training of human resources that will design, develop, produce, and utilize the technology that Industry 4.0 expects from us in every field is an inevitable reality. The realities of Industry 4.0 are individuals with high-level thinking skills; methods where mere knowledge will not suffice, and thinking will become mandatory.Additionally, Industry 4.0 will ensure that wastewater treatment facilities, which are a very important part of smart factories, operate much more reliably and stably. Thanks to next-generation sensors, important wastewater pollution parameters such as pH level in chemical treatments or oxygen level, COD, nitrogen, phosphorus, heavy metals, sulfur, sulfate, and cyanide in biological treatments can be easily measured, and values can be monitored for output.The cleanliness of the water will ensure that its impact on the environment remains stable, that is, harmless. Thus, moving towards an industrialization that is in harmony with nature and the ecological system, leaving a beautiful world for future generations is one of the most important issues of the upcoming period.It is of great importance to train individuals who will accurately sense and define global problems, generate innovative ideas for solutions, and use the right methods and techniques for solutions in every field. This situation should be considered, planned, designed, and implemented in a very broad perspective, integrating and interacting with each other, from preschool, primary education, secondary education, higher education, and lifelong learning.Sources;https://stumejournals.com/journals/i4/2016/2/141.full.pdf
https://tr.wikipedia.org
https://www.endustri40.com






